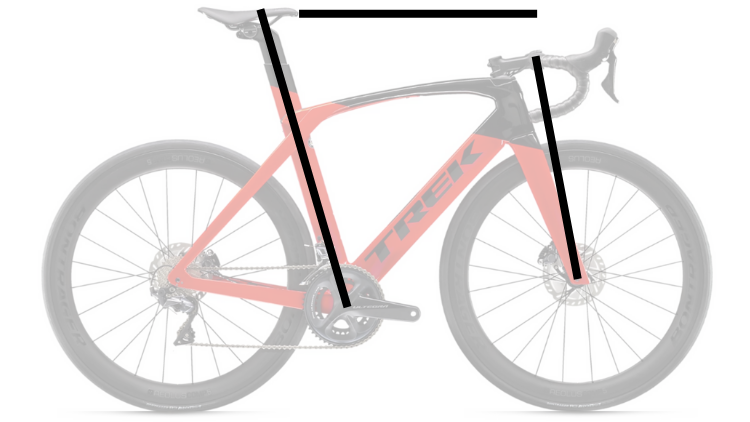

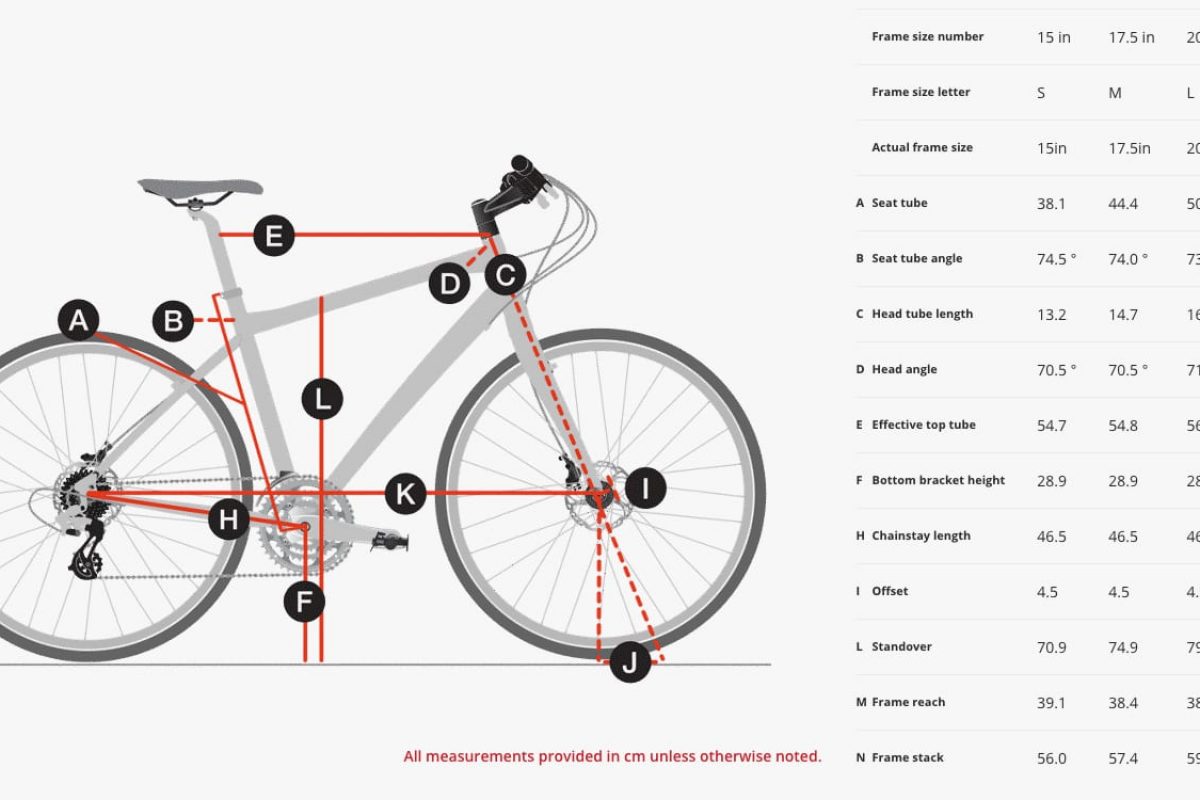

Penny-farthing frames are characterized by a large front wheel and a small rear wheel. Folding įolding bicycle frames are characterized by the ability to fold into a compact shape for transportation or storage. Examples include Humbers, Pedersens, and the one pictured.Ī monocoque frame consists only of a hollow shell with no internal structure. Truss Ī truss frame uses additional tubes to form a truss. The uncommon prone bike moves the cranks to the rear of the rider, resulting in a head-forward, chest-down riding position.Ī cross frame consists mainly of two tubes that form a cross: a seat tube from the bottom bracket to the saddle, and a backbone from the head tube to the rear hub. Banned from bicycle racing in France in 1934 to avoid rendering diamond-frame bicycles obsolete in racing, manufacturing of recumbent bicycles remained depressed for another half century, but many models from a range of manufacturers were available by 2000. The recumbent bicycle moves the cranks to a position forward of the rider instead of underneath, generally improving the slipstream around the rider without the characteristic sharp bend at the waist used by racers of diamond-frame bicycles. The seat stays connect the top of the seat tube (often at or near the same point as the top tube) to the rear fork ends. The chain stays run connecting the bottom bracket to the rear fork ends. It consists of the seat tube and paired chain stays and seat stays. The rear triangle connects to the rear fork ends, where the rear wheel is attached. The down tube connects the head tube to the bottom bracket shell. The top tube may be positioned horizontally (parallel to the ground), or it may slope downwards towards the seat tube for additional stand-over clearance. The top tube connects the head tube to the seat tube at the top. The head tube contains the headset, the interface with the fork. The rear triangle consists of the seat tube joined by paired chain stays and seat stays. In the diamond frame, the main "triangle" is not actually a triangle because it consists of four tubes: the head tube, top tube, down tube and seat tube. Besides the ubiquitous diamond frame, many different frame types have been developed for the bicycle, several of which are still in common use today.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
